Sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxation is a common effective policy adopted by governments to deter the purchase and consumption of SSBs. In the last decade, more than 50 countries worldwide have introduced a tax on SSBs. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends SSB taxes as a best buy[1] option for governments, noting that “just as taxing tobacco helped to reduce tobacco use, taxing sugary drinks can reduce consumption of sugar” (2017). Evidence of SSB tax effectiveness is published in a World Bank 2020 report that details the results of SSB taxes in jurisdictions across the globe. Overall, trends indicate that where taxes are enforced, purchases of SSBs decline. Furthermore, the higher the tax rate the greater the impact on consumer behaviour.
In the Caribbean, Barbados, Bermuda and Dominica have implemented SSB taxes. According to the World Bank report, Barbados implemented a 10% tax on SSBs in 2015 and in the first year, average weekly sales of SSBs overall and carbonated SSBs specifically decreased by 4.3% and 3.6%, respectively. Additionally, sales of non-SSBs increased 5.2%, with bottled water increasing 7.5%. In 2022, the Barbados government decided to increase the SSB tax to 20% after researchers found that some consumers shifted to purchasing cheaper SSB options instead of reducing consumption altogether. According to the WHO, to maximise the desired impact of SSB taxation, a minimal tax rate of 20% is recommended.
In Mexico, where SSB taxes higher than 10% were introduced in 2014, data show that three years after implementation, the excise tax on SSBs helped to increase the proportion of people who do not consume SSBs. A 2020 research study found that before implementation, more than 50% of research participants were medium and high consumers of SSBs and less than 10% were non-consumers. After tax implementation, 43% of the population was categorised as medium and high consumers and the prevalence of non-consumers increased to 14% (BMJ, 2020). Notably, the reduction in SSB consumption after tax implementation also led to recorded health improvements among adolescents in Mexico. For every 10% increase in the city’s average price of an SSB, there was a significant 1.3% absolute decrease in both overweight or obesity prevalence for girls within two years of the SSB price change (JAMA Pediatrics, 2021).
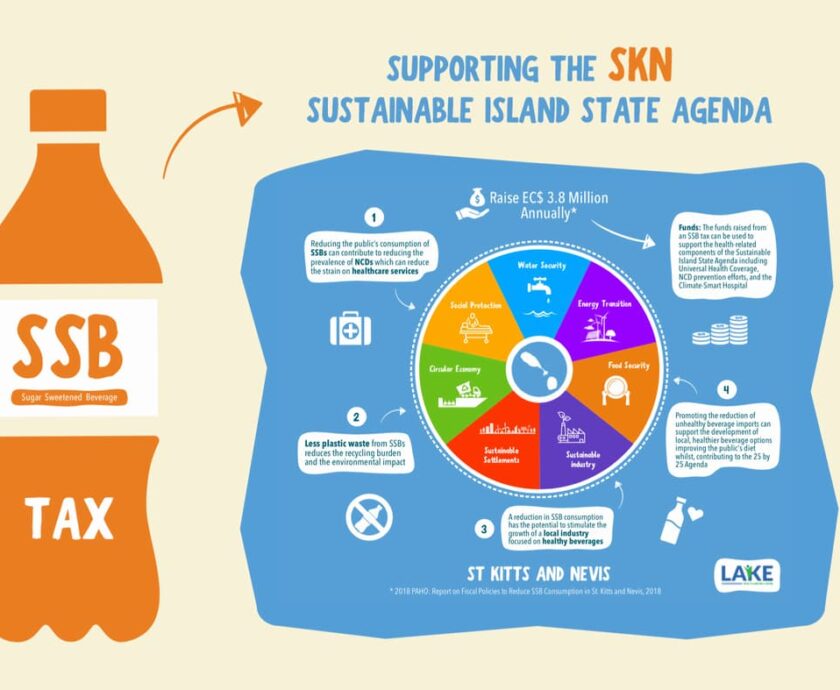
SSB taxation is a win-win solution. Evidence shows that taxation not only helps to reduce consumption which contributes to improved health over time, but it also generates additional government revenue which can be used to fund other necessary health promotion programmes. In Bermuda, SSB tax revenue was reinvested into making healthy foods more accessible by subsidising fruits and vegetables to increase consumption. In addition to healthy food subsidies, SSB tax jurisdictions in the United States report using revenue to invest into early childhood programmes and community infrastructure improvements like recreation centres and public gym parks to promote physical activity (PMR, 2021).
Public support for SSB taxes varies widely by jurisdiction, although when governments commit to designating tax revenue to reinvest into improving public health, general support for taxation increases. For instance, in St. Kitts and Nevis, public opinion polls completed in 2021 reveal that support for implementing SSB taxes across the federation increases if tax revenue is earmarked for investment in health-focused initiatives like improving public water drinking infrastructure. As an evidence-based policy solution SSB taxation is strongly recommended to reduce the consumption of sugary drinks and ultimately help to reduce the prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Government is not only being called to act but is encouraged to consider how SSB tax revenue can be designated to increase healthcare resources and improve public health outcomes.
[1] NCD Best-Buys are evidence-based public health interventions for tackling NCDs, according to the World Health Organization